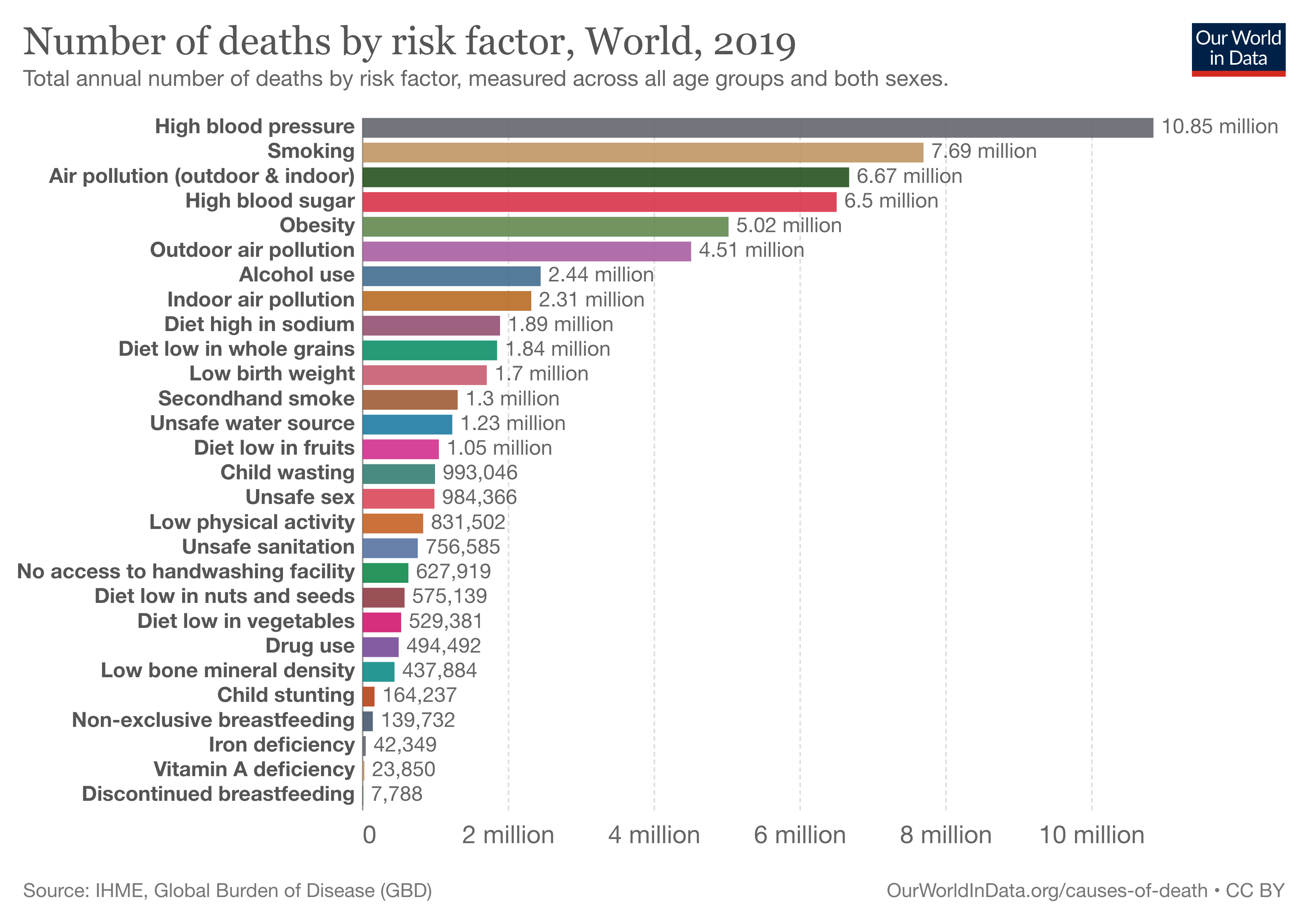
Air Pollution
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere. Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution

Air Pollution Data Portal
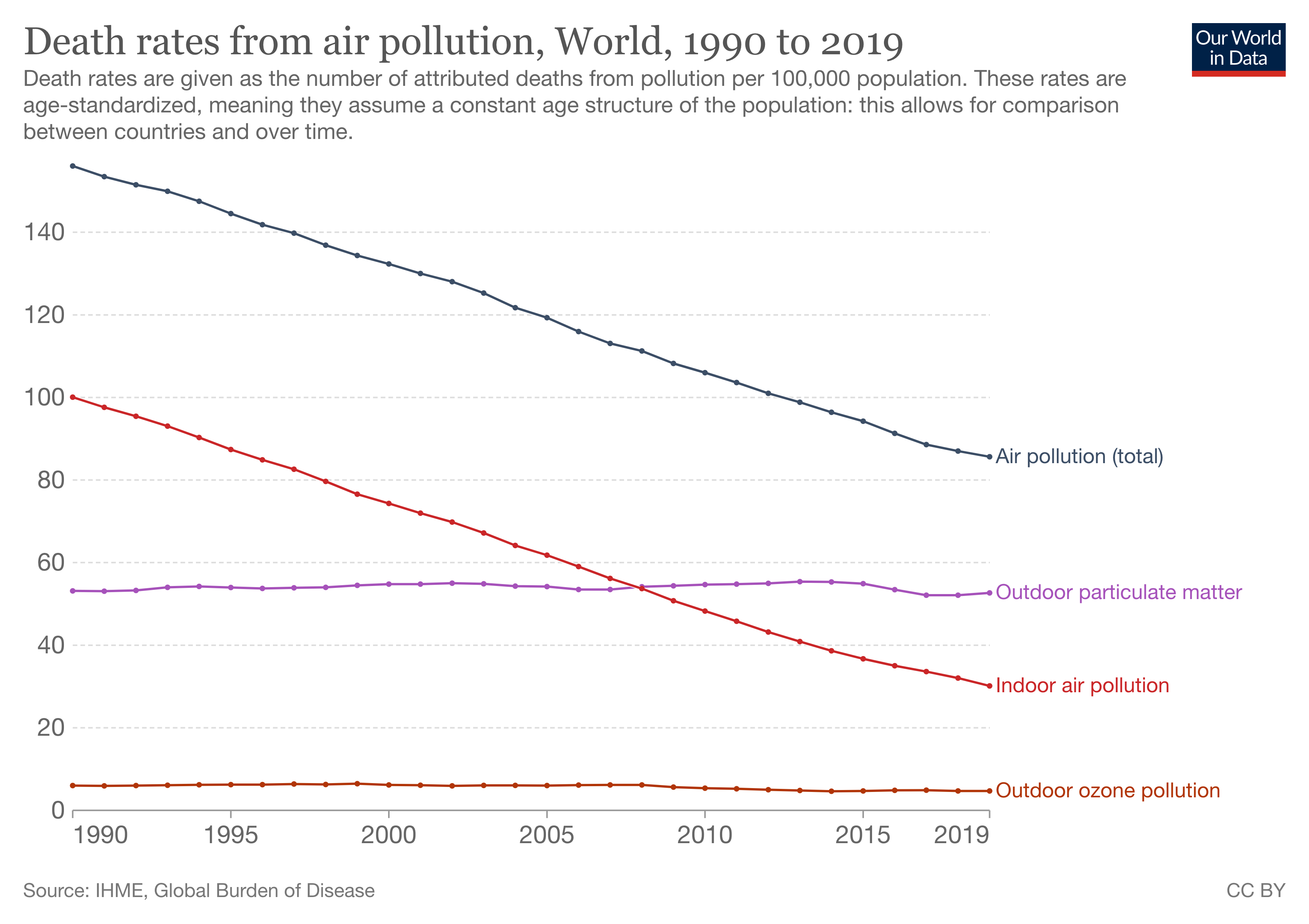
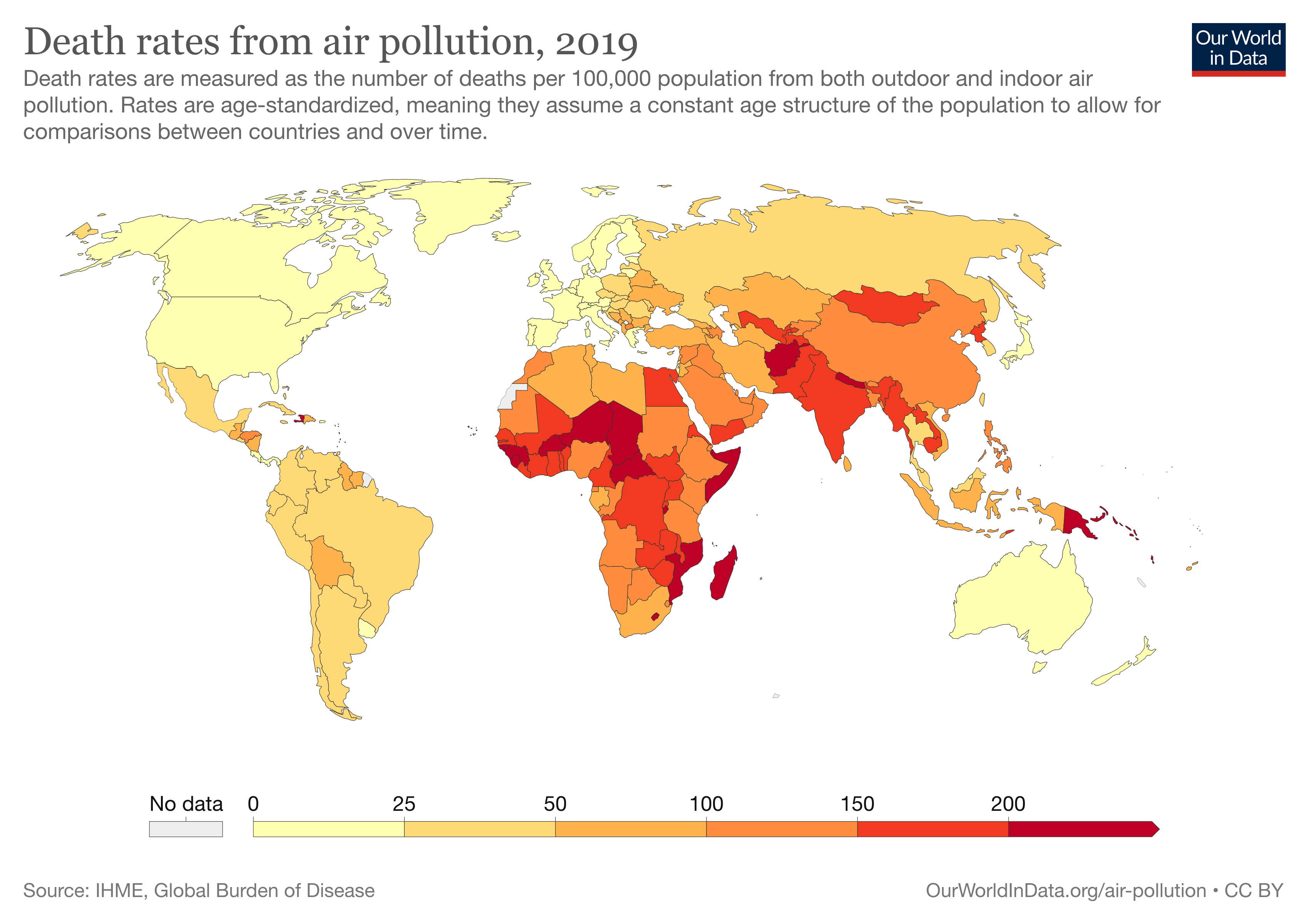
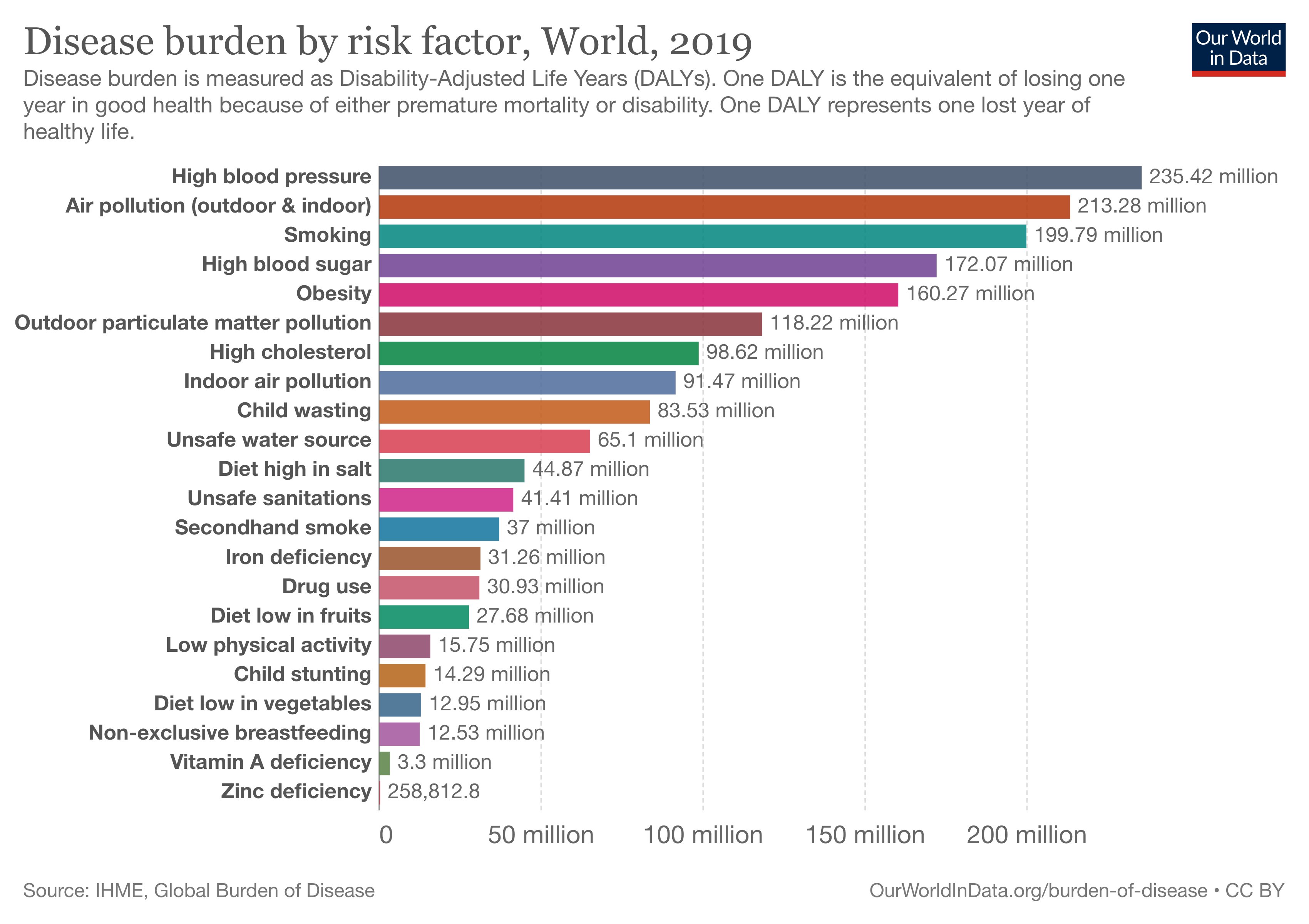
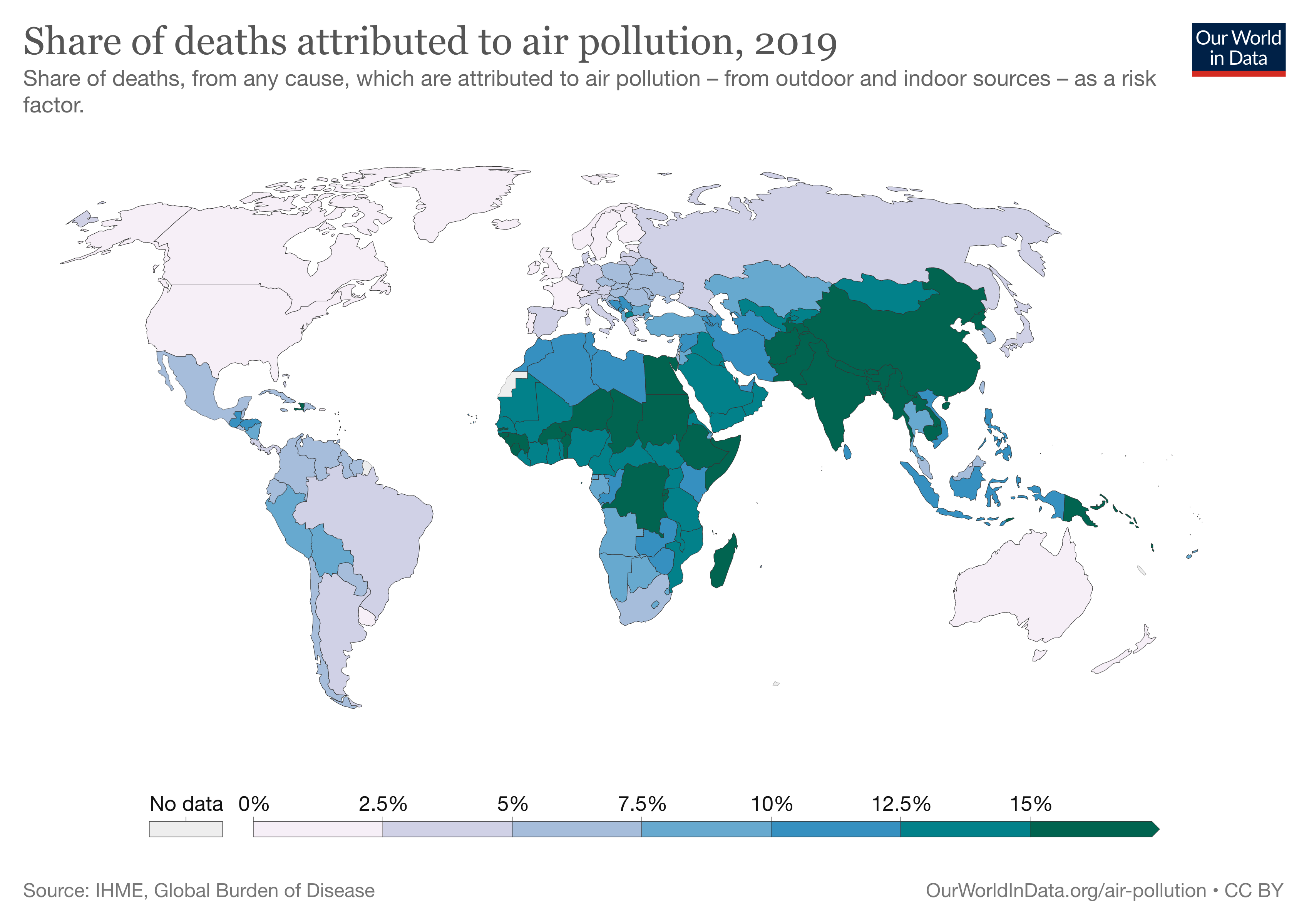
From smog hanging over cities to smoke inside the home, air pollution poses a major threat to health across the globe. Almost all of the global population (99%) are exposed to air pollution levels that put them at increased risk for diseases including heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer and pneumonia. WHO monitors the exposure levels and health impacts (i.e. deaths, DALYs) of air pollution at the national, regional and global level from ambient (outdoor) and household air pollution.
Burden of disease
7 million
deaths each year from exposure to ambient and household air pollution
Household exposure
2.6 million
people primarily rely on polluting fuels and technologies for cooking
Ambient exposure
91%
of the world's population live in places where air pollution levels exceeds WHO guideline limits
Air Quality Index
0 - 50
Good
51 - 100
Moederate
101 - 150
Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups
151 - 200
Unhealthy
201 - 300
Very Unhealthy
300+
Hazardous
References
- https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/air-pollution
- https://ourworldindata.org/air-pollution#:~:text=Air%20pollution%20is%20attributed%20to,in%20rates%20across%20the%20world.